Transection is a term used to describe follicular unit damage that occurs during harvesting and makes the unit unsuitable for transplantation. A follicular unit is a group of between one and four hair follicles that is harvested surgically or robotically from a donor area, collected, and transplanted into areas of hair loss. And, though hair restoration procedures have high success and patient satisfaction rates, all patients should be aware of what the process itself entails, and understand the estimated percentage of follicular units that may be lost to transection during harvesting.
FUE is a commonly performed, minimally-invasive minor surgical procedure for patients with androgenetic alopecia, often referred to as male pattern baldness. It is now the preferred method of hair restoration nationwide, and is suitable for male and female patients experiencing hair loss. This precise surgery involves the meticulous selection, harvesting, and grafting of follicular units. Understanding the anatomy of the hair follicle, and its vulnerabilities, is a key factor. So, to achieve excellent preservation of hair grafts, patients should choose a competent, experienced surgeon for their procedure and the right technology that minimizes transection.
Double board-certified surgeon Goran Jezic M.D. offers both the ATERA FUE and automated NeoGraft hair transplantation procedures for his patients at Houston Hair Transplant Center. Dr. Jezic creates personalized FUE treatment plans to enable his patients to regain fuller, thicker hair coverage and high regrowth success rates. Book your in-person or virtual consultation to discuss your hair restoration treatment by calling (713) 864-2300 or by filling out a simple online inquiry form.
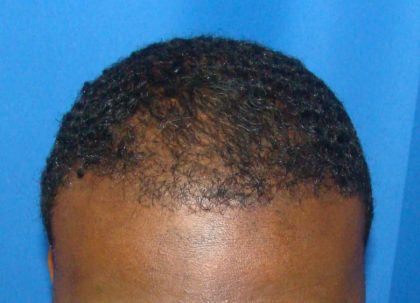
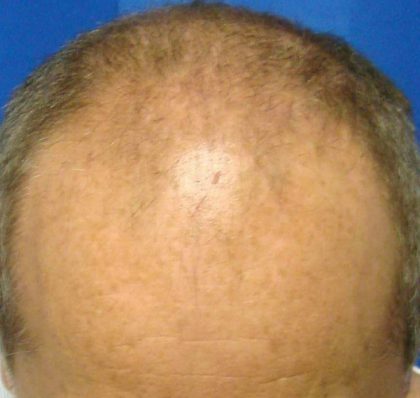
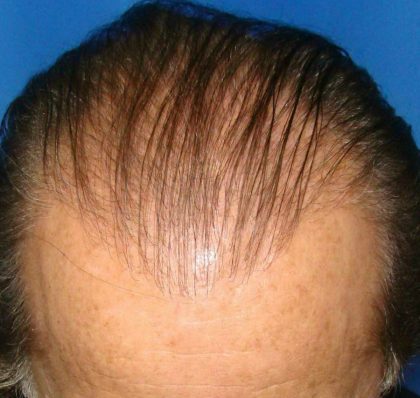
Before and After Photos
Transection & FUE
Transection is the accidental trauma caused to a hair graft during the hair restoration procedure, specifically the harvesting and extraction process during the procedure. If one or more hair follicles in a follicular unit is damaged, the graft cannot be preserved and will not be suitable for transplantation. Therefore, it’s important that the patient’s donor hair will survive the hair restoration process.
About Hair Loss
The familiar signs of thinning hair above the forehead and at the top of the head can indicate hair loss that will steadily progress in a predictable pattern on the scalp. The condition causes the hair follicles to shrink in a process known as follicular miniaturization. It also causes a shorter anagen, or growing, phase in the hair growth cycle. This means hair follicles become thinner and shorter. (1)
It can be distressing to lose one’s hair, the effects of which can cause embarrassment, a loss of confidence, and can even lead to feelings of depression and anxiety. Therefore, hair transplantation can be a life-changing procedure for many.
The Follicular Unit
Follicular units are natural clusters of hairs harvested for transplantation. In order to achieve success in hair grafting, an understanding of the anatomy of hair follicles themselves and how easily they can be affected by trauma is important. Each hair in the follicular unit has the following attributes.
Shaft – The hair shaft is the visible portion of the hair. It is made from compacted keratin. It is composed of three layers; the cuticle, the cortex, and the medulla.
Root – The hair root is the portion of the hair that is below the skin. Together with surrounding structures, the root forms the anchoring point of the hair in the skin.
Bulb – The bulb and the lower portion of the hair are deeply embedded in the deepest layers of the skin; the hypodermis and the dermis.
Papilla – The hair papilla is a delicate area at the bottom of the bulb that connects to the blood supply. Cells in the hair papilla play a crucial role in hair formation and growth.
Pilosebaceous Unit – The hair is anchored by the follicle itself and two other structures; the arrector pili muscle and the sebaceous gland. The arrector pili muscle raises the hair to generate heat when we are cold, while the sebaceous gland secretes oil known as sebum.
Root Sheath – Visible when the follicular unit is harvested, the root sheath is a thick, translucent covering of connective tissue that surrounds the follicle.
One of the most important areas of the hair follicle is the hair bulb, which contains the hair papilla. The papilla, surrounded by protective connective tissue, is important to preserve because it is the part of the hair that connects to the blood supply. If the hair bulb is cut, or transected, it cannot be implanted successfully into the donor area.
How Can Grafts Become Damaged?
About 10% of hair follicles exit the scalp singly when harvested. They may also be harvested in groups of between 2-5 follicles. (2) There are many factors that affect the survival rate of hair grafts in the transplantation process. These include:
- Mechanical trauma – Blunt trauma from medical instruments can occur during harvesting or transplantation. This is the precise meaning of a transected graft, whereby the hair is physically damaged, therefore unable to be grafted successfully.
- Donor area scalp issues – Where the hair is unsuitable because it is fine, sparse, or weak. The surgeon must ensure that donor sites are carefully selected.
- Dehydration – Dehydrated hair follicles will not transplant successfully. Dehydration can make grafts brittle and more susceptible to damage.
- ATP depletion – ATP provides energy to cells. ATP depletion can negatively affect graft survival rates.
- Hypoxia – Hypoxia is a lack of oxygenation. A condition known as ischaemia–reperfusion injury occurs when grafts experience a lack of oxygen when they are harvested, causing a sudden onset of hormones at the hair follicle after transplantation that limits viability.
Transection Rates
A transection rate is the percentage of follicular units lost to extraction-related mechanical trauma. Transection rates vary from patient to patient and surgeon to surgeon. It is the surgeon’s responsibility to assess a patient’s suitability for a hair transplant procedure, and it’s the patient’s responsibility to understand that a small percentage of the grafts harvested will be transected. Studies show that FUE transection rates are heavily dependent on harvesting skill, technique and technology. An inexperienced team may have a transection rate of over 20%, whereas an experienced hair transplant doctor’s transection rate may be 2% or less. On average, it is estimated that between 5-10% of grafts will be transected during a hair transplant procedure. (3) This rate may be reduced to under 5%, or even 2%, with semi-automated extraction methods such as ATERA FUE. Note that the graft count received by the client reflects how many grafts were implanted/transplanted excluding the ones that were transected. Therefore, transection does not impact clients. If a client paid for 2,000 grafts and the transection rate is let’s say 10%, then at least 2,200 grafts would be harvested in order to get to the 2,000 target.
Reasons For Transection
FUE involves the use of special tools called punches which are used to harvest donor hair. These punches come in different sizes, sharpness, compositions and designs, and may vary in appearance according to their manufacturer. The anatomy of the follicle, the properties of the punch, and how the punch is applied by the harvester affect the ability to harvest follicular units with high survival rates. Factors that affect transection rates include the following.
- Graft quality
- The fluid dynamics of the follicle
- Inadequate size punch
- Inappropriate force applied
- Incorrect punch orientation
- Inaccurate angle of insertion (4)
FUE at Houston Hair Transplant Center
ATERA FUE
ATERA FUE is an advanced, minimally-invasive graft harvesting system. It uses a handpiece controlled by the surgeon that has a tube feature attached. Once extracted, the follicular units are sucked into the tube which leads to an enhanced follicle collection system that preserves each graft. This system keeps each graft moist and cool before transplantation.
ATERA Benefits
- Efficient hair transplantation
- No “strip” scarring in the donor area
- Multiple punch sizing options for individualized treatment
- Preservation method limits mechanical damage
- Lubricated grafts for maximum preservation
- Digital graft counter monitors the number of grafts harvested
Dr. Jezic may recommend ATERA FUE based on your donor hair quality. He will determine your eligibility for treatment at a personal consultation at his Houston facility. Please see our website for more information about the cost of ATERA FUE.
NeoGraft
NeoGraft is a hair transplantation system that significantly improves speed and accuracy in the graft harvesting process. It allows for the automated harvesting of individual hair follicles from the back of the head which is guided by the surgeon. Like ATERA, NeoGraft is minimally-invasive and does not lead to a visible strip scar on the scalp.
NeoGraft Benefits
- Semi-automated method for fast, accurate extraction
- Automation limits graft transection
- Ergonomic device is a “natural extension” of surgeon’s hand
- Shorter overall procedure compared to ARTAS
- No “strip” scarring in the donor area
- Rapid, comfortable healing
- For more information about NeoGraft, please see our NeoGraft FAQ.
To find out if NeoGraft or ATERA is suitable for your needs, schedule your initial consultation with Dr. Jezic. Patients outside the area are welcome to inquire about a virtual consult.
Personal Consultation
To find out if NeoGraft or ATERA hair transplantation is a good fit for your hair loss needs, please schedule a consultation with Houston Hair Transplantation. Dr. Jezic sees all patients one-on-one to ask questions related to their hair loss, examine the areas of the scalp for treatment, and assess optimal donor areas. Please contact us for more information about scheduling your first appointment with us.
To see real results, please visit the Houston Hair Transplantation social media pages on Facebook, Instagram, and YouTube. You can also find out more about follicular unit extraction by reading Dr. Jezic’s blog.
Cost of a Hair Transplant in Houston
The cost of FUE hair restoration is determined according to the technology/technique used and the price per graft. We will calculate an estimate for your treatment following your initial consultation with Dr. Jezic. Don’t let hair loss get you down. Book your appointment by calling (713) 864-2300, or by filling out our simple inquiry form.
References
- Ho CH, Zito PM. Androgenetic Alopecia. Nih.gov. Published May 18, 2019. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK430924/
- Parsley WM, Perez-Meza D. Review of factors affecting the growth and survival of follicular grafts. Journal of cutaneous and aesthetic surgery. 2010;3(2):69-75. doi:10.4103/0974-2077.69014 https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2956960/#:~:text=Important%20factors%20include%20the%20patient’s,efforts%20to%20increase%20graft%20survival.
- Dua A, Dua K. Follicular unit extraction hair transplant. Journal of cutaneous and aesthetic surgery. 2010;3(2):76-81. doi:10.4103/0974-2077.69015 https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2956961/
- Sharma R, Ranjan A. Follicular Unit Extraction (FUE) Hair Transplant: Curves Ahead. Journal of Maxillofacial & Oral Surgery. 2019;18(4):509-517. doi:10.1007/s12663-019-01245-6 https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6795649/